Walking asymmetry refers to an uneven gait pattern where steps differ in timing, length, or force between the left and right sides. Minor, inconsistent asymmetry is common and often benign. However, significant or persistent asymmetry can indicate underlying health issues.
Health Implications of Significant Walking Asymmetry
Pronounced gait asymmetry is rarely normal and frequently points to neuromuscular or musculoskeletal problems:
- Neurological Conditions: Stroke, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), cerebral palsy, peripheral neuropathy.
- Musculoskeletal Pain or Injury: Severe osteoarthritis (especially hip or knee), joint replacements, ligament/muscle tears (e.g., ACL, plantar fascia), fractures, chronic ankle instability, leg length discrepancy.
- Pain: Significant pain in the back, hip, knee, ankle, or foot inherently leads to compensatory asymmetry.
- Balance Disorders: Vestibular problems affecting inner ear function.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Intermittent claudication (leg pain due to poor circulation).
- Cognitive Decline: Emerging research links increasing gait asymmetry to early stages of cognitive impairment.
When to Be Concerned and Talk to Your Doctor
Consult a healthcare professional if you notice:
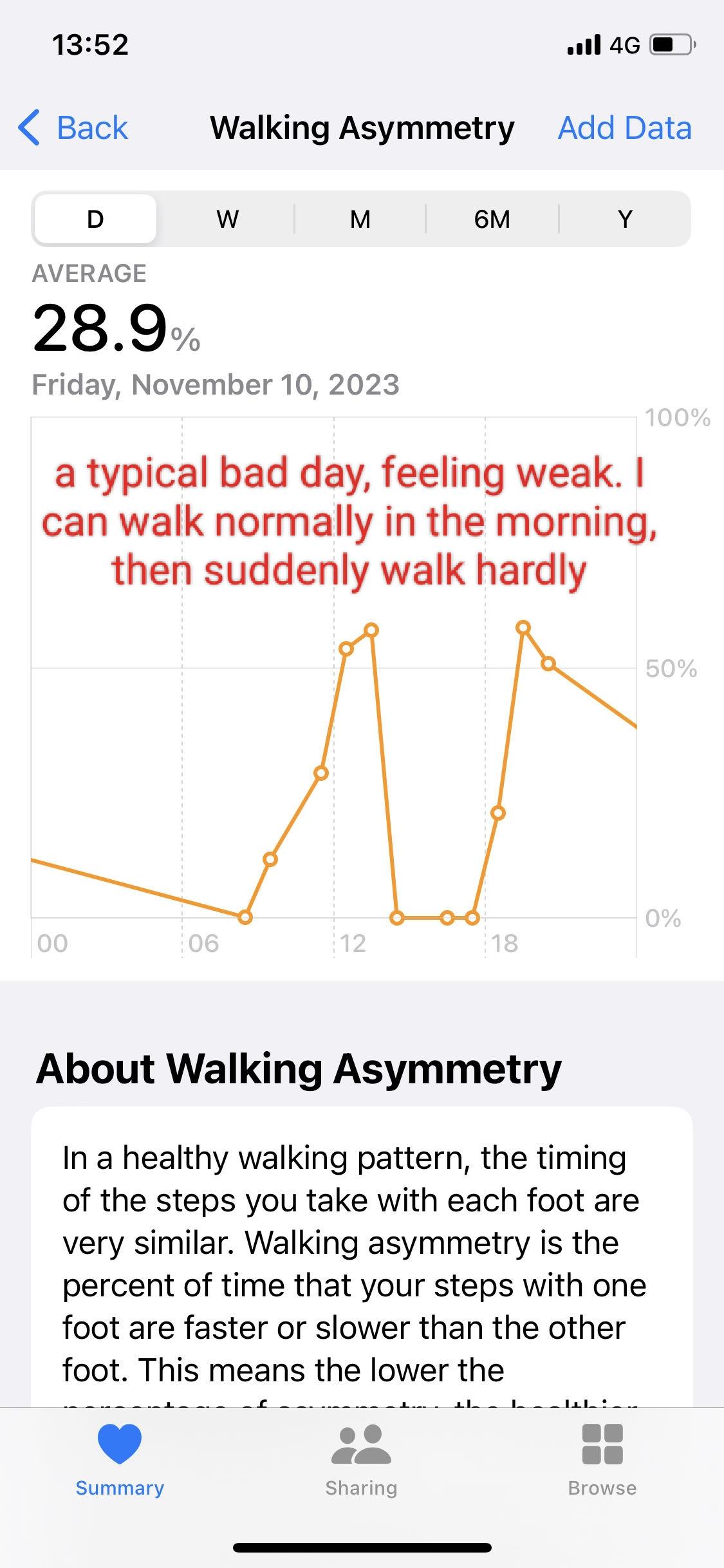
- Sudden Onset: Asymmetry appearing abruptly, especially after a fall or injury.
- Progressive Worsening: A noticeable increase in unevenness over time.
- Associated Symptoms: Accompanied by pain, numbness, tingling, weakness, dizziness, unexplained fatigue, significant stiffness, or balance problems.
- Impact on Function: Difficulty walking, increased falls or near-falls, reduced walking speed/distance, or reliance on aids (cane, walker) when previously not needed.
- Persistent Asymmetry: Noticeable unevenness lasting for several weeks without improvement.
Seek urgent medical attention for asymmetry combined with:
- Sudden severe weakness (especially on one side).
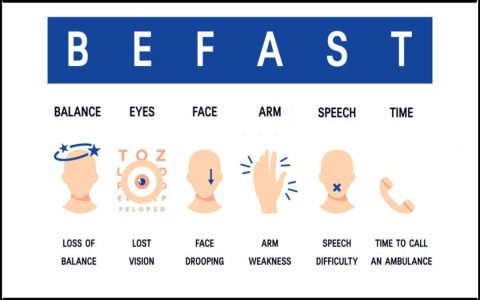
- Sudden severe headache, confusion, vision changes, or slurred speech (possible stroke).
- Obvious deformity or inability to bear weight after trauma.
Early assessment of significant walking asymmetry is crucial for accurate diagnosis and timely intervention to address the underlying cause and prevent complications like falls or further decline.